A more polite Taylor Swift with NLP and word vectors
My relation with Taylor Swift is complicated: I don't hate her — in fact, she seems like a very nice person. But I definitely hate her songs: her public persona always comes up to me as entitled, abusive, and/or an unpleasant person overall. But what if she didn't have to be? What if we could take her songs and make them more polite? What would that be like?
In today's post we will use the power of science to answer this question. In particular, the power of Natural Language Processing (NLP) and word embeddings.
The first step is deciding on a way to model songs. We will reach into our
NLP toolbox and take out
Distributional
semantics, a research area that
investigates whether words that show up in similar contexts also have similar
meanings. This research introduced the idea that once you treat a word like a
number (a vector, to be precise, called the embedding of the word), you
can apply regular math operations to it and obtain results that make sense.
The classical example is a result shown in
this paper, where
Mikolov and his team managed to represent words in such a way that the
result of the operation King - man + woman ended up being very
close to Queen.
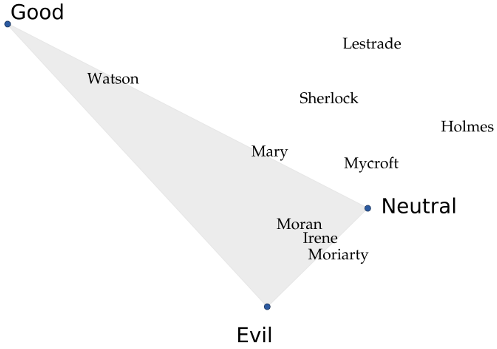
The picture below shows an example. If we apply this technique to all the Sherlock Holmes novels, we can see that the names of the main characters are placed in a way that intuitively makes sense if you also plot the locations for "good", "neutral", and "evil" as I've done. Mycroft, Sherlock Holmes' brother, barely cares about anything and therefore is neutral; Sherlock, on the other hand, is much "gooder" than his brother. Watson and his wife Mary are the least morally-corrupt characters, while the criminals end up together in their own corner. "Holmes" is an interesting case: the few sentences where people refer to the detective by saying just "Sherlock" are friendly scenes, while the scenes where they call him "Mr. Holmes" are usually tense, serious, or may even refer to his brother. As a result, the world "Sherlock" ends up with a positive connotation that "Holmes" doesn't have.
This technique is implemented by
word2vec, a series of
models that receive documents as input and turn their words into vectors.
For this project, I've chosen the
gensim Python library. This
library does not only implement word2vec but also
doc2vec, a model that will do all the heavy-lifting for us when it
comes to turn a list of words into a song.
This model needs data to be trained, and here our choices are a bit limited. The biggest corpus of publicly available lyrics right now is (probably) the musiXmatch Dataset, a dataset containing information for 327K+ songs. Unfortunately, and thanks to copyright laws, working with this dataset is complicated. Therefore, our next best bet is this corpus of 55K+ songs in English, which is much easier to get and work with.
The next steps are more or less standard: for each song we take their words,
convert them into vectors, and define a "song" as a special word whose meaning
is a combination of its individual words. But once we have that, we can start
performing some tests. The following code does all of this, and then asks an
important question: what would happen if we took Aerosmith's song
Amazing,
removed the
import csv
import gzip
from gensim.models import Doc2Vec
from gensim.models.doc2vec import TaggedDocument
documents = []
with gzip.open('songlyrics.zip', 'r') as f:
csv_reader = csv.DictReader(f)
counter = 0
# Read the lyrics, turn them into documents,
# and pre-process the words
for row in csv_reader:
words = simple_preprocess(row['text'])
doc = TaggedDocument(words, ['SONG_{}'.format(counter)})
documents.append(doc)
counter += 1
# Train a Doc2Vec model
model = Doc2Vec(documents, size=150, window=10, min_count=2, workers=10)
model.train(document, total_examples=len(documents), epochs=10)
# Apply some simple math to a song, and obtain a list of the 10
# most similar songs to the result.
# In our lyrics database, song 22993 is "Amazing", by Aerosmith
song = model['SONG_22993']
query_vector = song - model['amazing']
for song, vector in model.docvecs.most_similar([query_vector]):
print(song)
One would expect that
- ...Margarita, a song about a man who meets a woman in a bar and cooks soup with her.
- ...Alligator, a song about an alligator lying by the river.
- ...Pony Express, a song about a mailman delivering mail.
We can use this same model to answer all kind of important questions I didn't know I had:
- Have you ever wondered what would be "amazingly lame"? I can tell you!
Amazing +lame = History in the making, a song where a rapper tells us how much money he has. - Don't you think sometimes "I like
We
are the World, but I wish it had more
violence ?". If so, Blood on the World's hands is the song for you. - What if we take Roxette's
You
don't understand me and add
understanding to it? As it turns out, we end up with It's you, a song where a man breaks up with his wife/girlfriend because he can't be the man she's looking for. I guess he does understand her now but still: dude, harsh. - On the topic of hypotheticals: if we take John Lennon's
Imagine
and we take away the
imagination , all that's left is George Gershwin's Strike up the band, a song about nothing but having "fun, fun, fun". On the other hand, if we added even moreimagination we end up with Just my imagination, dreaming all day of a person who doesn't even know us.
This is all very nice, but what about our original question: what if we took Taylor Swift's songs and removed all the meanness? We can start with her Grammy-winning songs, and the results are actually amazing: the song that best captures the essence of Mean minus the meanness is Blues is my middle name, going from a song where a woman swears vengeance to a song where a man quietly laments his life and hopes that one day things will come his way. Adding politeness to We are never coming back together results in Everybody knows, a song where a man lets a woman know he's breaking up with her in a very calm and poetic way. The change is even more apparent when the bitter Christmases when you were mine turns into the (slightly too) sweet memories of Christmas brought by Something about December.
Finally, and on the other side, White Horse works better with the anger in. While this song is about a woman enraged at a man who let her down, taking the meanness out results in the hopeless laments of Yesterday's Hymn.
So there you have it. I hope it's clear that these are completely accurate results, that everything I've done here is perfectly scientific, and that any kind of criticism from Ms. Swift's fans can be safely disregarded. But on a more serious note: I hope it's clear that this is only the tip of the iceberg, and that you can take the ideas I've presented here in many cool directions. Need a hand? Let me know!
Further reading
- Piotr Migdal has written a
popular
post about why the
King - man + woman = Queenanalogy works, including an interactive tool. - The base for my code was inspired by
this
tutorial on the use of
word2vec. - The good fellows at FiveThirtyEight used this technique to analyze what Trump supporters look like, applying the technique to the news aggregator Reddit.
The problem with music recommendations
There's a popular song, written by an Argentinean musician called Charly García, called "Los Dinosaurios" ("The Dinosaurs"). The song was released in 1983 in the album "Clics Modernos", and you can listen to it in all its vinyl glory here.
This song represents for me an interesting problem: it is by far my favourite song from this author, and I would like to listen to something similar. But so far all recommendation systems have failed me. Here are some of the reasons why.
A first approach could be to pick something from the same author, or even the same album. This approach, sadly, doesn't work: while Charly García is certainly a prolific author, with 41 published records and countless guest appearances, his main style is oriented towards electronic music, and it doesn't really fit the style of this specific song. If anything, this song is more fitting for his earlier albums, which limits us quite a bit - out of those 41 soloist albums, "Clics Modernos" is the second one.
We could instead assume that this song was written in a certain context, and that looking at authors from a similar context we can obtain similar music. Again, this doesn't entirely work: if we pick "Argentinean songs from the 80's", we would end up with a list of songs that fit perfectly the style of the other 8 songs on this album, but not this one specifically^1. Grouping the song into "Latin American music", as some systems do, only exacerbates the problem: there is no relation at all between this song and, say, a Cuban bachata.
If we look at the actual lyrics, the situation gets even worse: "Los dinosaurios" is a thinly veiled critique of the military dictatorship that ruled the country between 1976 and 1983. A lyrics-based systems would most likely fail on two fronts: either it wouldn't understand the references made in the song and label it as "nonsense/fantastical", or it would understand the reference and recommend politically charged songs. Neither approach seems really right - while "The times they are a-Changin" could be a viable candidate for a recommendation, neither "The Revolution will not be televised" nor "Redemption song" fit the bill.
All of these approaches fail for the same reason: they apply a network-oriented measure to a song that doesn't fit the popular rhythm of the time and place in which it was produced, and which doesn't fit the overall style of the author either.
So what exactly am I looking for? A non-technical answer would be "I need a song that contains simple vocals, a piano as it's main instrument, and with raising tension towards the end". Or in the words of the author, a song that "adapts the English sound to Tango". As far as I know, the only system that applied a similarity measure capable of detecting this would be Pandora, but with their system closed to Europe, I cannot tell whether this works or not.
Footnotes
^1 How to obtain a digital archive of Argentinean songs from the early 80's is left as an exercise for the reader.
Related reading:
Guitar music and I
Here's a joke I heard once at a music academy:
How do you keep a pianist from playing? You take away their music sheet.
How do you keep a guitarist from playing? You give them a music sheet.
This joke rings oh-so-true because it highlights a key point for those of us who tried to learn guitar by ourselves: the typical amateur guitar player doesn't know how to read music, and (s)he doesn't care about it. Somehow they manage, but how they do that remains a mistery to me.
Typical guitar tabs (those you buy at a shop or download from the internet) contain therefore little more than the lyrics for a song and the points at which you are supposed to switch from one chord to another. This works pretty well for your left hand, but how about the right one? Should I just move it up and down? And at which speed? "Well", says the guitar book, "you should just do whatever feels natural". This is of course useless - what am I, the song whisperer? What if nothing feels natural? Do I just sit there in silence?
Let's take the following example, which I borrowed from Ultimate-guitar.com
RHYTHM FOR INTRO AND VERSE:
D G A
E|--2--2-2-0-2---2-3-2-0-2--3--3-3--0--0--0-0-0-0-0---|
B|--3--3-3-3-3---3-3-3-3-3--3--3-3--2--2--2-3-2-2-2---|
G|--0--0-0-0-0---0-0-0-0-0--0--0-0--2--2--2-2-2-2-2---|
D|--------------------------2--2-2--0--0--0-0-0-0-0---|
A|--------------------------3--3-3--------------------|
INTRO
D G A [play twice]
VERSE 1:
D
You'll say
G A D
we got nothing in common
G A D
no common ground to start from
G A D G A
and we're falling apart
This is actually a fairly complete piece: it shows the lyrics and notes (lower half) along with an attempt at explaining how should the strumming (i.e., what to do with your right hand) be performed. But here's the thing: it's not clear at all which strokes should be "up" and "down", nor the duration and silences between them. You cannot derive rhytm from this information, which is pretty bad for a section titled "Rhytm for intro and verse". And here's an extra fact: the "D" section should actually be played exactly the same as the "G A" section, but good luck discovering that from this notation. This is a known bug of guitar tabs, and yet I have several books with songs that don't even include such a section, either because they don't care or because they realized it's useless.
This is one of those very few problems that is currently solved by, of all things, Youtube. It's not too hard to find a "How to play Breakfast at Tiffany's" video tutorial, where some dude will spend some time showing you slow motion strumming, so you can play the whole thing. But how come youtubers have fixed this problem so fast, while guitar books have remained the same for decades? Why isn't everybody complaining? My theory is that the typical amateur guitarist picks up a guitar, downloads one of these tabs, fails at getting anything out of it, and quits guitar forever saying "guitars are hard".
I don't really have a good solution, because any attempt at formalizing the strumming will undoubtedly require some knowledge about rhytm, and guitar players seem to hate that. Perhaps that's how we ended up in this mess in the first place. Or perhaps there's a super easy, totally intuitive method that I've always missed for one reason or another.
But then again: how can a method do any good if it's never taught?
